A telecommunications network is a group of nodes (node is an electronic device that is attached to a network, and is capable of creating, receiving, or transmitting information) interconnected by links (link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission.) that are used to exchange messages between the nodes.
Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Telecommunications facilitates interaction and information transfer over
large distances. Businesses use telecommunications to expand and grow
their networks. With Internet, computer, and telephone networks,
businesses can allocate their resources efficiently.
Computer Network
Computer network is a telecommunication channel using which we can share data with other computers or devices, connected to the same network. It is also called Data Network. The best example of computer network is Internet.
Computer network does not mean a system with one Control Unit connected to multiple other systems as its slave. That is Distributed system, not Computer Network.
A network must be able to meet certain criteria s, these are mentioned below:
- Performance
- Reliability
- Scalability
Computer Networks: Performance
It can be measured in the following ways:
- Transit time : It is the time taken to travel a message from one device to another.
- Response time : It is defined as the time elapsed between enquiry and response.
Other ways to measure performance are :
- Efficiency of software
- Number of users
- Capability of connected hardware
Computer Networks: Reliability
It decides the frequency at which network failure take place. More the failures are, less is the network's reliability.
Computer Networks: Security
It refers to the protection of data from any unauthorised user or access. While travelling through network, data passes many layers of network, and data can be traced if attempted. Hence security is also a very important characteristic for Networks.
Basic Communication Model
A Communication model is used to exchange data between two parties. For example: communication between a computer, server and telephone (through modem).

Communication Model: Source
Data to be transmitted is generated by this device, example: telephones, personal computers etc.
Communication Model: Transmitter
The data generated by the source system is not directly transmitted in the form its generated. The transmitter transforms and encodes the data in such a form to produce electromagnetic waves or signals.
Communication Model: Transmission System
A transmission system can be a single transmission line or a complex network connecting source and destination.
Communication Model: Receiver
Receiver accepts the signal from the transmission system and converts it into a form which is easily managed by the destination device.
Communication Model: Destination
Destination receives the incoming data from the receiver.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Data Communication
The exchange of data between two devices through a transmission medium is called Data Communication. The data is exchanged in the form of 0's and 1's. The transmission medium used is wire cable. For data communication to occur, the communication device must be a part of a communication system. Data Communication has two types - Local and Remote which are discussed below:
Data Communication: Local
Local communication takes place when the communicating devices are in the same geographical area, same building, or face-to-face etc.
Data Communication: Remote
Remote communication takes place over a distance i.e. the devices are farther. The effectiveness of a data communication can be measured through the following features :
- Delivery: Delivery should be done to the correct destination.
- Timeliness: Delivery should be on time.
- Accuracy: Data delivered should be accurate.
Components of Data Communication
- Message: It is the information to be delivered.
- Sender: Sender is the person who is sending the message.
- Receiver: Receiver is the person to whom the message is being sent to.
- Medium: It is the medium through which the message is sent. For example: A Modem.
- Protocol: These are some set of rules which govern data communication.
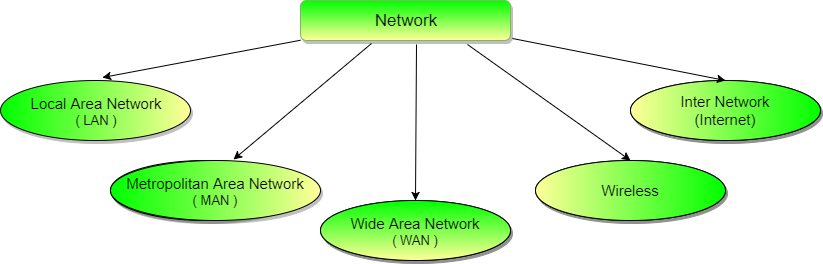
Types of Telecommunication Networks
Communication Networks can be of following 5 types:
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Wireless
- Inter Network (Internet)
Local Area Network (LAN)
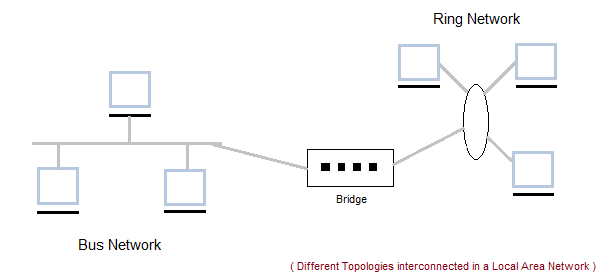
It is also called LAN and designed for small physical areas such as an office, group of buildings or a factory. LANs are used widely as it is easy to design and to troubleshoot. Personal computers and workstations are connected to each other through LANs. We can use different types of Topologies through LAN, these are Star, Ring, Bus, Tree etc.
LAN can be a simple network like connecting two computers, to share files and network among each other while it can also be as complex as interconnecting an entire building.
LAN networks are also widely used to share resources like printers, shared hard-drive etc.
Characteristics of LAN
- LAN's are private networks, not subject to tariffs or other regulatory controls.
- LAN's operate at relatively high speed when compared to the typical WAN.
- There are different types of Media Access Control methods in a LAN, the prominent ones are Ethernet, Token ring.
- It connects computers in a single building, block or campus, i.e. they work in a restricted geographical area.
Applications of LAN
- One of the computer in a network can become a server serving all the remaining computers called clients. Software can be stored on the server and it can be used by the remaining clients.
- Connecting Locally all the workstations in a building to let them communicate with each other locally without any internet access.
- Sharing common resources like printers etc are some common applications of LAN.
Advantages of LAN
- Resource Sharing: Computer resources like printers, modems, DVD-ROM drives and hard disks can be shared with the help of local area networks. This reduces cost and hardware purchases.
- Software Applications Sharing: It is cheaper to use same software over network instead of purchasing separate licensed software for each client a network.
- Easy and Cheap Communication: Data and messages can easily be transferred over networked computers.
- Centralized Data: The data of all network users can be saved on hard disk of the server computer. This will help users to use any workstation in a network to access their data. Because data is not stored on workstations locally.
- Data Security: Since, data is stored on server computer centrally, it will be easy to manage data at only one place and the data will be more secure too.
- Internet Sharing: Local Area Network provides the facility to share a single internet connection among all the LAN users. In Net Cafes, single internet connection sharing system keeps the internet expenses cheaper.
Disadvantages of LAN
- High Setup Cost: Although the LAN will save cost over time due to shared computer resources, but the initial setup costs of installing Local Area Networks is high.
- Privacy Violations: The LAN administrator has the rights to check personal data files of each and every LAN user. Moreover he can check the internet history and computer use history of the LAN user.
- Data Security Threat: Unauthorised users can access important data of an organization if centralized data repository is not secured properly by the LAN administrator.
- LAN Maintenance Job: Local Area Network requires a LAN Administrator because, there are problems of software installations or hardware failures or cable disturbances in Local Area Network. A LAN Administrator is needed at this full time job.
- Covers Limited Area: Local Area Network covers a small area like one office, one building or a group of nearby buildings.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
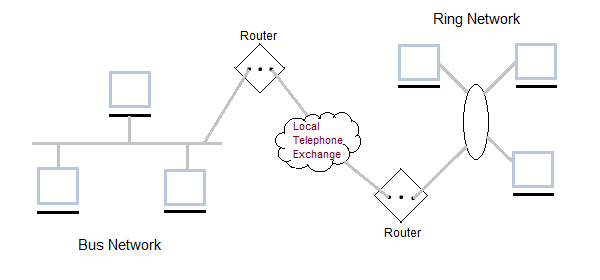
It was developed in 1980s.It is basically a bigger version of LAN. It is also called MAN and uses the similar technology as LAN. It is designed to extend over the entire city. It can be means to connecting a number of LANs into a larger network or it can be a single cable. It is mainly hold and operated by single private company or a public company.
Characteristics of MAN
- It generally covers towns and cities (50 km)
- Communication medium used for MAN are optical fibers, cables etc.
- Data rates adequate for distributed computing applications.
Advantages of MAN
- Extremely efficient and provide fast communication via high-speed carriers, such as fibre optic cables.
- It provides a good back bone for large network and provides greater access to WANs.
- The dual bus used in MAN helps the transmission of data in both directions simultaneously.
- A MAN usually encompasses several blocks of a city or an entire city.
Disadvantages of MAN
- More cable required for a MAN connection from one place to another.
- It is difficult to make the system secure from hackers and industrial espionage(spying) graphical regions.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
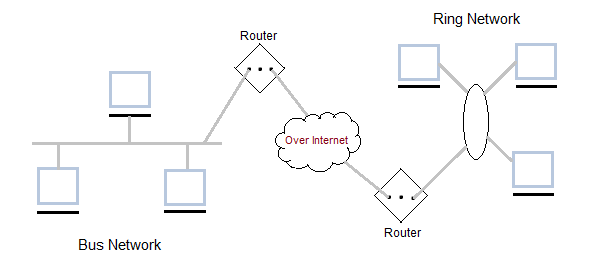
It is also called WAN. WAN can be private or it can be public leased network. It is used for the network that covers large distance such as cover states of a country. It is not easy to design and maintain. Communication medium used by WAN are PSTN or Satellite links. WAN operates on low data rates.
Characteristics of WAN
- It generally covers large distances(states, countries, continents).
- Communication medium used are satellite, public telephone networks which are connected by routers.
Advantages of WAN
- Covers a large geographical area so long distance business can connect on the one network.
- Shares software and resources with connecting workstations.
- Messages can be sent very quickly to anyone else on the network. These messages can have picture, sounds or data included with them(called attachments).
- Expensive things(such as printers or phone lines to the internet) can be shared by all the computers on the network without having to buy a different peripheral for each computer.
- Everyone on the network can use the same data. This avoids problems where some users may have older information than others.
Disadvantages of WAN
- Need a good firewall to restrict outsiders from entering and disrupting the network.
- Setting up a network can be an expensive, slow and complicated. The bigger the network the more expensive it is.
- Once set up, maintaining a network is a full-time job which requires network supervisors and technicians to be employed.
- Security is a real issue when many different people have the ability to use information from other computers. Protection against hackers and viruses adds more complexity and expense.
Wireless Network
Digital wireless communication is not a new idea. Earlier, Morse code was used to implement wireless networks. Modern digital wireless systems have better performance, but the basic idea is the same.
Wireless Networks can be divided into three main categories:
- System interconnection
- Wireless LANs
- Wireless WANs
System Interconnection
System interconnection is all about interconnecting the components of a computer using short-range radio. Some companies got together to design a short-range wireless network called Bluetooth to connect various components such as monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer, to the main unit, without wires. Bluetooth also allows digital cameras, headsets, scanners and other devices to connect to a computer by merely being brought within range.
In simplest form, system interconnection networks use the master-slave concept. The system unit is normally the master, talking to the mouse, keyboard, etc. as slaves.
Wireless LANs
These are the systems in which every computer has a radio modem and antenna with which it can communicate with other systems. Wireless LANs are becoming increasingly common in small offices and homes, where installing Ethernet is considered too much trouble. There is a standard for wireless LANs called IEEE 802.11, which most systems implement and which is becoming very widespread.
Wireless WANs
The radio network used for cellular telephones is an example of a low-bandwidth wireless WAN. This system has already gone through three generations.
- The first generation was analog and for voice only.
- The second generation was digital and for voice only.
- The third generation is digital and is for both voice and data.
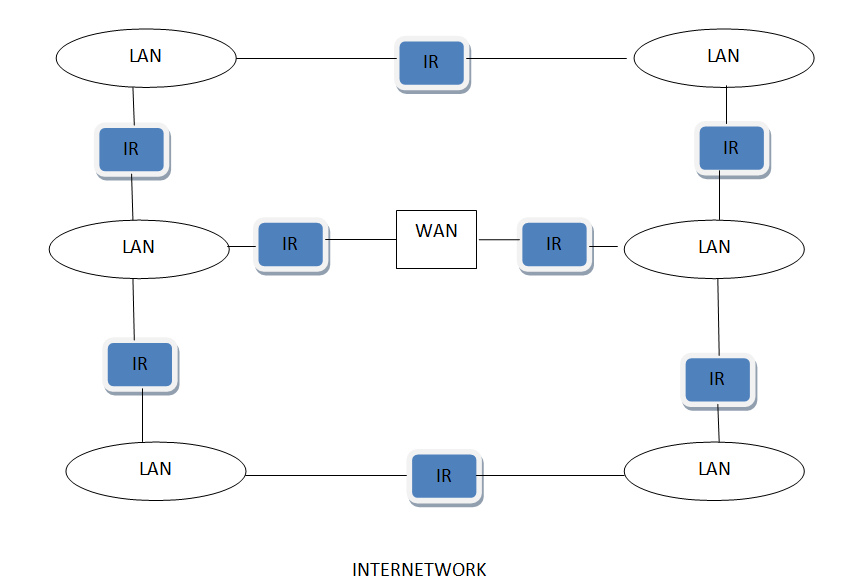
Inter Network / INTERNET
Inter Network or Internet is a combination of two or more networks. Inter network can be formed by joining two or more individual networks by means of various devices such as routers, gateways and bridges.
Internet network: access to the network allows users to use many
resources. Over time the Internet network will replace books. This will
enable users to discover information almost instantly and apply concepts
to different situations. The Internet can be used for recreational,
governmental, educational, and other purposes. Businesses in particular
use the Internet network for research or to service customers and
clients.
Telephone network: the telephone network connects people to one another.
This network can be used in a variety of ways. Many businesses use the
telephone network to route calls and/or service their customers.























